
Austempering
Austempering is the heat treatment applied for medium to high carbon steels, usually to Steels containing Si, Cr, Mo ,Mn and B, where a metallurgical structure called beynite is obtained.
The fractions are heated to austenite zone (815-950 ° C), then the martensite is cooled sufficiently quickly to a temperature above the initial (Ms) temperature (230-400 ° C) and salt is removed for a sufficient time to obtain the desired bainite microstructure. kept in the bath.
Tempering after austempering is not required. Because the desired hardness of the part is obtained from the salt bath cooling temperature following the heating process. Other types of heat treatment require tempering, as the parts come out with a higher hardness than the required hardness and must be softened to the specification.
Quenching at higher temperatures for austempering hardening greatly reduces the risk of distortion of parts compared to quenching in oil. This is because it significantly slows down cooling of the cooling elements at higher temperatures, rather than at lower temperatures, such as in oil. Slower cooling results in less stress on the parts due to thermal expansion and shrinkage, and less stress on conversion.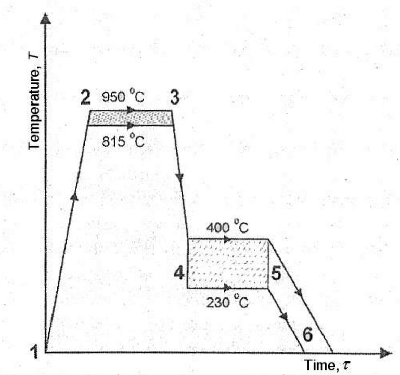
Advantages of Altavox's Austempering Process:
»Less distortion
»High ductility
»Due to the clean surface in the salt quenching process, the parts are easily coated
»Smooth and consistent hardness
»Harder and more wear-resistant
»Higher impact and fatigue strength
»Resistance to hydrogen embrittlement
»Provides higher corrosion resistance.
You should use the Austempering process if:
»Material thickness from 0.008 to 0.150 inches
»Hardness requirements between HRC 38-58
»Distortion prone
»Continuous load materials
Applied Materials:
C45, CK45, C50, C55, CK55, C60, CK60, C67, C67S, CK67, C70, C75, CK75, 4130, 4140, 5060, 5160, 6150, 51CrV4,

 Select Language
Select Language 








